Antibody Engineering: Innovations and Applications in Biomedicine
Introduction:
Antibody engineering has emerged as a powerful field within biomedicine, allowing for the development of novel antibody-based therapeutics, diagnostics, and research tools
.By modifying the structure and function of antibodies, researchers are able to enhance their specificity, stability, and therapeutic efficacy, opening up new possibilities for precision medicine.
Engineering Antibodies for Therapeutic Applications:
One of the key areas of antibody engineering is the development of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for therapeutic use. These antibodies are designed to target specific antigens, such as cancer cells or inflammatory molecules, while minimizing side effects on healthy tissues.
Engineering techniques include antibody humanization, where non-human antibodies are modified to be more similar to human antibodies, and antibody optimization for enhanced binding affinity and stability.
Principle of Engineered Antibodies:
Enhance effector function potency and half-life through Fc modification.
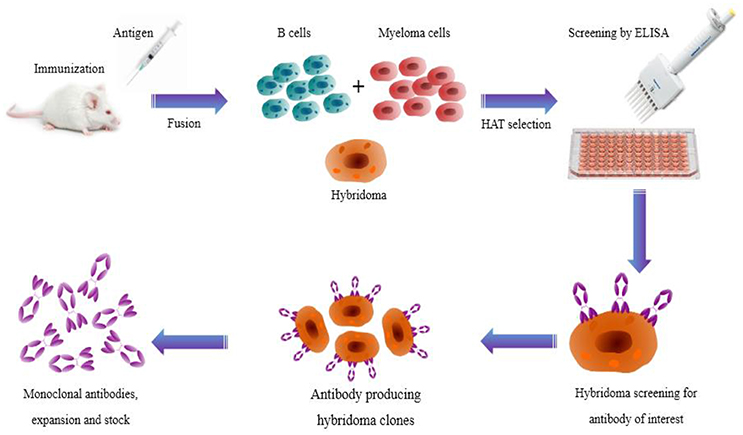
Reduce or eliminate bystander effects. Isolate and express antibody genes using single B-cell cloning or combinatorial libraries.
Allow enlargement of the antibody repertoire and focused on possibilities.
Applications of Engineered Antibodies:
Engineered antibodies have revolutionized the treatment of various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. They are used as targeted therapies to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells, sparing healthy tissues from damage.
Additionally, engineered antibodies are used in diagnostics to detect the presence of specific molecules, such as biomarkers for disease.
Future Directions:
The field of antibody engineering continues to evolve, with ongoing research focused on improving antibody design, delivery, and specificity.
Emerging technologies such as bispecific antibodies, which can bind to two different targets simultaneously, are expanding the therapeutic possibilities of antibody-based therapies.
