441
Bordetella pertussis/B.parapertussis/B.bronchiseptica RT-PCR (CE) | B84-100FRT
- SKU:
- 441-B84-100FRT-GEN
- Availability:
- IN STOCK
Description
Bordetella pertussis/B.parapertussis/B.bronchiseptica RT-PCR | B84-100FRT is available for delivery
Description:
General information: Real Time PCR kit for detection and typing of Bordetella
Target Disease Type: Respiratory Infections
Specific Application: Bordetella pertussis
Storage and Shipping : 4 weeks
Bordetella pertussis/B.parapertussis/B.bronchiseptica RT-PCR (CE) B84-100FRT DataSheet
INTRODUCTION
Bordetella is a genus of small (0.2 - 0.7 µm), Gram-negative coccobacilli of the phylum proteobacteria. Three species are human respiratory pathogens (B. pertussis, B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica).
Bordetella pertussis is an obligate human pathogen and is the causative agent of whooping cough (pertussis). Bordetella parapertussis causes a milder form of disease in humans and also causes respiratory infections in sheep. Bordetella bronchiseptica has the broadest host range, causing disease in many mammalian species, but kennel cough in dogs and atrophic rhinitis, in which infected piglets develop deformed nasal passages, have the biggest economic impact.
Humans, however are rarely infected with this organism. When infections in humans occur, they are often acquired through animal contact and typically involve immunocompromised patients. The spectrum of immunocompromised patients who have developed B.bronchiseptica infection includes patients with malignancies such as Hodgkin's disease, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, cardiac and bone marrow transplantation patients,patients with AIDS.
INTENDED USE
Bordetella pertussis/B. parapertussis/B. bronchiseptica Real-TMPCR kit is an in vitro nucleic acid amplification test for detection and differentiation of pathogens that cause whooping cough (Bordetella pertussis), parapertussis (Bordetella parapertussis), and Bordetella bronchiseptica infection (Bordetella bronchiseptica) in the clinical materials (nasal and oropharyngeal swabs) and culture of microorganisms by using real-time hybridization-fluorescence detection.
PRINCIPLE OF ASSAY
Bordetella determination by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with hybridization fluorescent detection includes three stages: DNA extraction from clinical samples, PCR-amplification of pathogen genome specific region and real-time hybridization fluorescent detection. DNA is extracted from samples in presence of Internal Control (IC), which allows to monitor the analysis of each sample. In real-time PCR, the amplified product is detected using fluorescent dyes.
These dyes are linked to oligonucleotide probes which bind specifically to the amplified product during thermocycling. The real-time monitoring of the fluorescence intensities during the real-time PCR allows the detection of PCR product without re-opening the reaction tubes after the PCR run.
During the amplification stage, four simultaneous reactions take place – amplification of the conservative region of ptxA gene that codes pertussis toxin located in Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica genomes; identification of specific regions in genomes of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica as well as amplification of nucleic acid sequence of the Internal Control (IC) sample:
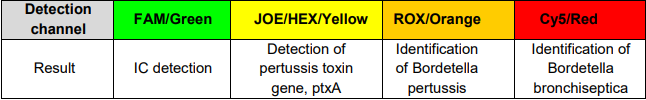
In case of pertussis toxin gene detection (JOE/HEX/Yellow channel), the conclusion about presence of Bordetella spp. (B.pertussis, B.parapertussis or B.bronchiseptica) is made.
If results are concurrently positive both in JOE/HEX/Yellow and ROX/Orange channels, the sample is considered positive for Bordetella pertussis.
If results are concurrently positive both in JOE/HEX/Yellow and Cy5/Red channels, the sample is considered positive for Bordetella bronchiseptica.
Presence of Bordetella parapertussis can be concluded in case of pertussis toxin gene detection (JOE/HEX/Yellow channel) in the sample negative for Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica providing that sufficient Bordetella DNA is available.






