Description
Dityrosine (DT) ELISA
A novel biomarker for protein oxidation
Tyrosine is one of the major targets of protein oxidation, and until today various tyrosine derivatives such as nitrotyrosine, dityrosine and halogenated tyrosine depending on the type of free radicals. DT is a tyrosine dimer derived from tyrosyl radicals which is formed by reactive oxygen species (ROS), metal-catalyzed oxidation, ultraviolet irradiation, and peroxidases. DT have been found in atherosclerotic lesions, and lipofuscin of pyramidal neurons of aged human brains. Dityrosine is one of the specific biomarkers for protein oxidation.
Recently, dityrosine is reported to exist also in urine samples. It is expected that DT may be a novel protein oxdation marker, which is non-invasively detectable. DT ELISA kit is designed for quantitative measurement of DT especially in urine samples.
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
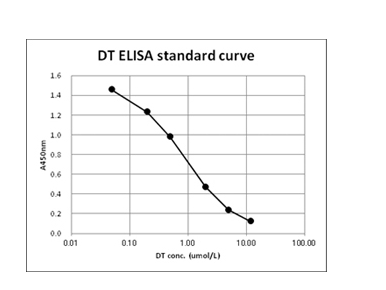
Additional Information
Size: |
96 wells |
Type of Marker: |
Protein oxidation |
Marker: |
Dityrosine (Tyr dimer) |
Storage: |
Less than -20°C |
Usage: |
Tissue |
Application: |
Immunohistochemistry, western blotting and ELISA |






