Description
Mannitol Salt Agar | DM160D
A selective medium for the isolation of pathogenic staphylococci.
Following the observation by Koch1 that usually only staphylococci are able to grow on 7.5% salt agar, Chapman2 described the use of Mannitol Salt Agar for the differential isolation of pathogenic staphylococci. It is worth noting that Gunn et al3 improved the medium by the addition of 2% egg yolk which identified 94.7% of coagulase producing strains. Recent work has shown that some strains of staphylococci may be partially inhibited by the high level of sodium chloride in Chapman's medium.4,5 To overcome this, the medium has been modified by reducing the sodium chloride concentration from 7.5 to 3.0%. Inhibition of Gram negative bacilli has been maintained by the inclusion of Lithium chloride. Pyruvate and glycine are included as growth promoters to enhance the recovery of S.aureus from samples containing small numbers of the organism.6,7 The medium is suitable for use with Oxacillin Selectatab™ (MS29) for the detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using the method described by Lally et al8
.
Directions
1. Suspend by swirling 76g of powder in 1 litre or the contents of the sachet in the stated volume of distilled or deionised water.
2. Autoclave at 121ºC (15p.s.i.) for 15 minutes.
3. Mix well before pouring.
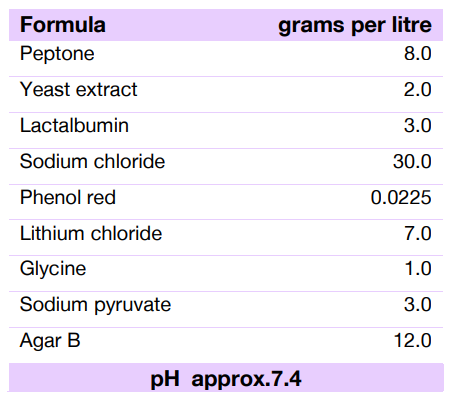
Technical Formula
In Use
Inoculate plates by spreading the sample over the surface of the medium and incubate at 37ºC for up to 48 hours. Pathogenic
staphylococci grow well and ferment mannitol, indicated by yellow zones around the colonies, whereas non-pathogenic staphylococci produce smaller white colonies indicating non-fermentation of mannitol.






