Description
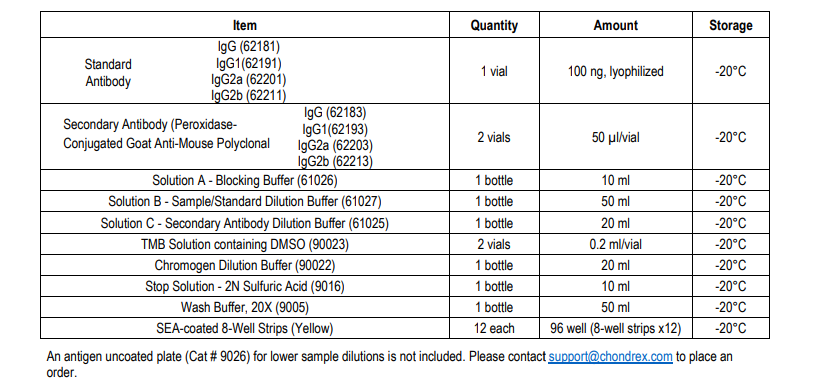
Mouse Anti-SEA IgG2a Antibody Assay Kit - Cat Number: 6220 From .
Research Field: Bacterial Research, Immunology
Clonality: N/A
Cross-Reactivity:
Host Origin: N/A
Applications: N/A
Isotype: N/A
Detection Range: 100 ng/ml-1.6 ng/ml
Sample Type: Serum, Plasma
Concentration: N/A
Immunogen:
DESCRIPTION: ELISA kits to quantify mouse anti-SEA IgG/IgG1/IgG2a/IgG2b antibodies
6218: Mouse Anti-SEA IgG Antibody ELISA Kit
6219: Mouse Anti-SEA IgG1 Antibody ELISA Kit
6220: Mouse Anti-SEA IgG2a Antibody ELISA Kit
6221: Mouse Anti-SEA IgG2b Antibody ELISA Kit
FORMAT: Pre-coated 96-well ELISA Plate with removeable strips
ASSAY TYPE: Indirect ELISA
ASSAY TIME: 4.5 hours
STANDARD RANGE: 100 ng/ml to 1.6 ng/ml
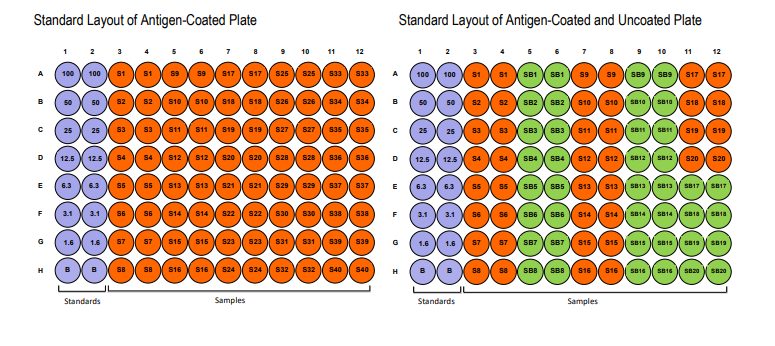
NUMBER OF SAMPLES: Up to 40 (duplicate) diluted samples/plate and up to 20 (duplicate) low dilution samples/plate
SAMPLE TYPES: Serum and Plasma
RECOMMENDED SAMPLE DILUTIONS: 1:200 (at least)
CHROMOGEN: TMB (read at 450 nm)
STORAGE: -20°C
VALIDATION DATA: 6218: Intra-assay (4.2-7.3%)/Inter-assay (1.4-10%)/Spiking Test (96-100%)
6219: Intra-assay (3.3-10%)/Inter-assay (3.3-8%)/Spiking Test (98-107%)
6220: Intra-assay (2.7-7.1%)/Inter-assay (1.4-2%)/Spiking Test (89-107%)
6221: Intra-assay (5.7-8.2%)/Inter-assay (1.3-7.2%)/Spiking Test (95-103%)
INTRODUCTION
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a gram-positive coccal bacterium frequently found in the human respiratory tract and on the skin. S. aureus infections contribute to a broad spectrum of illnesses, including endocarditis, septic arthritis, toxic-shock syndrome, scalded-skin syndrome, and food poisoning (1-4). Recently, antibiotic-resistant strains (e.g. methicillin-resistant S. aureus) are being isolated more frequently which presents a challenge to clinical medicine. This bacterium produces a variety of toxic exoproteins that can trigger massive pro-inflammatory cytokine release, leading to severe inflammation and tissue damage (5-7). Among these toxins, staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B (SEA and SEB) are known superantigens
that bridge MHC-class II molecules and T-cell receptors, resulting in a potent stimulation of the host immune system, which is believed to contribute to the pathogenicity of autoimmune diseases (8).
For instance, a study found that the presence of anti-SEA and anti-SEB IgE antibodies correlated with the severity of skin lesions in children with atopic dermatitis (9). SEA and SEB have also been used in vaccine development to protect against staphylococcal infections (5,6). Anti-SEA and/or SEB IgG antibodies may work as vaccine-induced, allergenspecific IgG antibodies to occupy the binding sites intended for IgE antibodies. To study the pathological roles of SEA and SEB in mice, , Inc. provides mouse anti-SEA IgG antibody and IgG subtype antibody ELISA kits (Cat # 6218 - 6221) and mouse anti-SEB IgG antibody and IgG subtype antibody ELISA kits (Cat # 6218 - 6221). In addition, , Inc. also provides a variety of antibody ELISA kits against various bacteria and toxins. Please visit www..com for more information. For further requests and consultation, please contact , Inc. at support@.com.
KIT COMPONENTS
IDENTIFICATION OF ANTIGEN-COATED STRIPS
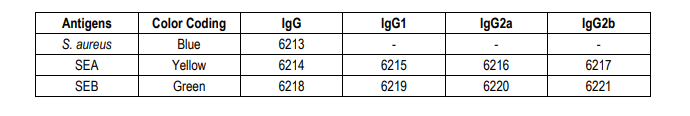
PLATE MAPPING
NOTES BEFORE USING ASSAY
NOTE 1: It is recommended that the standard and samples be run in duplicate.
NOTE 2: Warm up all buffers to room temperature before use.
NOTE 3: Crystals may form in Wash Buffer, 20X when stored at cold temperatures. If crystals have formed, warm the wash buffer by placing the bottle in warm water until crystals are completely dissolved.
NOTE 4: Measure exact volume of buffers using a serological pipet, as extra buffer is provided.
NOTE 5: Cover the plate with plastic wrap or a plate sealer after each step to prevent evaporation from the outside wells of the plate.
NOTE 6: For partial reagent use, please see the assay protocol’s corresponding step for the appropriate dilution ratio. For example, if the protocol dilutes 50 µl of a stock solution in 10 ml of buffer for 12 strips, then for 6 strips, dilute 25 µl of the stock solution in 5 ml of buffer. Partially used stock reagents may be kept in their original vials and stored at -20⁰C for use in a future assay.
NOTE 7: This kit contains animal components from non-infectious animals and should be treated as potential biohazards in use and for disposal.
ASSAY OUTLINE

ASSAY PROCEDURE
Add Blocking Buffer: Add 100 µl of the Blocking Buffer (Solution A) to each well and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature NOTE: If a sample with a dilution of 1:200 or less is assayed, antigen non-coated strips should be used. Solution A must be added to the non-coated wells without prior washing because any contaminants in the vessel containing the washing buffer will bind to the strips. For example, add 100 µl of Solution A to the antigen-coated strips (S1) and the corresponding uncoated strips (SB1).
Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. 2. Prepare Standard Dilutions: The recommended standard range is 1.6-100 ng/ml. Dissolve one vial of standard (100 ng/vial) in 1 ml Standard/Sample Dilution Buffer (Solution B) to make a 100 ng/ml stock standard solution. Then, serially dilute it with Solution B. For example, mix 250 ml of the 100 ng/ml solution with an equal volume of Solution B to make a 50 ng/ml solution, and then repeat it five more times for 25, 12.5, 6.3, 3.1, and 1.6 ng/ml standard solutions. The leftover standard stock may be kept at -20°C for future use.










